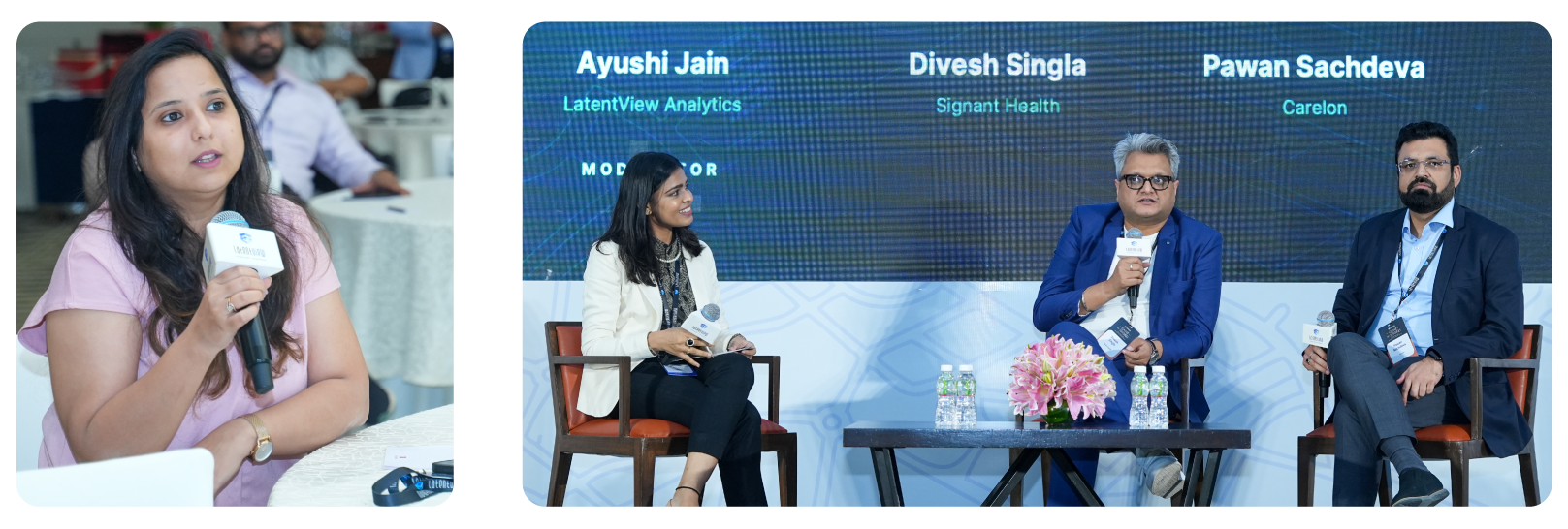
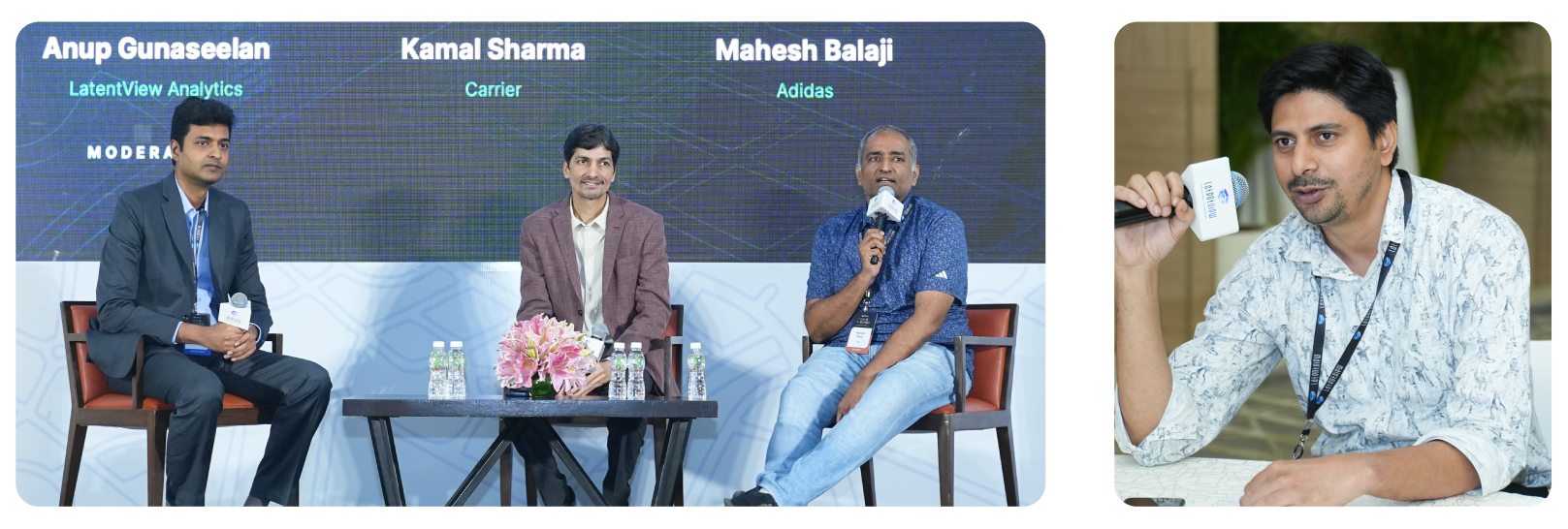
The evolving role of GCCs from cost-saving back offices to strategic innovation hubs is now on the fast track. India now hosts nearly 1,800 GCCs, with 24 crossing the $1 billion export revenue mark, reflecting a rapid transformation driven by value addition, not just scale.
India’s GCC market size is projected to grow from $64.6 billion in 2024 to $105 billion by 2030. Offshore support centers are evolving into global partners, driving digital transformation through AI-driven R&D, the new frontier of enterprise-wide innovation.
Data analytics and AI lie at the heart of the ongoing transformation, enabling GCCs to shift from hindsight to foresight. By converting vast amounts of operational data into actionable insights, GCCs are driving innovation and efficiency across diverse sectors. In product research and development, CPG companies leverage real-time consumer sentiment to accelerate new product innovation, while pharmaceutical firms harness AI to expedite drug discovery and streamline clinical trials. In risk management, leading banks such as Wells Fargo and Bank of America employ AI-powered predictive models to identify emerging risks, detect anomalies, and ensure regulatory compliance.
These developments reflect a broader trend of GCCs evolving from task-execution centers to strategic hubs that provide unified, real-time visibility across functions, accelerating enterprise-wide decision-making. Today, half of all GCCs operate as portfolio and transformation hubs, while 90% have expanded into multi-disciplinary centers that span technology, operations, finance, human resources, and marketing. Notably, Engineering and R&D activities now generate approximately half of GCC revenue, underscoring the central role these centers play in product engineering, intellectual property generation, and AI-driven innovation.
However, challenges remain, Rajan pointed out. Many GCCs still struggle to demonstrate value due to a slow rate of scaling, talent gaps, data quality issues, and regulatory complexities. To overcome these challenges, three key levers are:
- Change Management: Foster partnership between headquarters and GCC as co-creators of transformation
- Develop Local Leadership: Empower entrepreneurial leaders who bridge global vision and local execution
- Capacity Building: Invest in purpose-driven tech adoption, particularly AI/ML, with the support of capable partners
Specifically, emphasizing the talent gap, Rajan points out that this remains a core challenge for companies, as building the right team that possesses both domain and technical expertise can be an uphill task. Addressing these issues is critical for GCCs to fully realize their potential as indispensable drivers of business growth and innovation.
Scaling a GCC requires the right vision, the right people, and the right mandate —there’s no one-size-fits-all blueprint. Success depends on your organization’s risk appetite, readiness, and strategic goals. The popular models for setting up and scaling GCCs are: Do-It-Yourself for full autonomy, Partner-Supported for a faster, lower-risk entry that leverages local expertise, or Build-Operate-Transfer, which phases ownership to mitigate early risks. With abundant choices, companies need to consider which model suits them best.
In this journey, it’s not about who can scale the fastest but who can think to drive revenue streams. He concluded by urging GCCs to get their data in place so that innovation would follow and scaling would come with ease.